Introduction
Imaging and inspection projects require the use of precision optics and calibration to achieve optimal performance. The telecentric system uses key components such as imaging lens, light source, camera and mechanical device for machine vision inspection. The choice of imaging lens and camera is an important part of a successful application, but illumination is also important. Telecentric illumination is one of the most accurate illumination geometry types. What is telecentric illumination? How does telecentric illumination help produce better results? To answer these questions, we need to consider illumination concepts, advantages, and real-world inspection applications.
Principle of telecentric illumination
Telecentricity is a unique feature of some multi-element lens designs in optics, where the main light is aligned and parallel to the axis of the image and object. A key feature of telecentricity is that it provides constant magnification regardless of the location of the image or object. The telecentric lenses are divided into three types: object-space, image-space, and bi-telecentric lenses.
Telecentric illuminators use optical principles to direct light from optical fibers or LEDs onto a detection object, producing a high contrast profile. They reduce the diffuse reflection of the object, thus improving the edge contrast and measuring accuracy. Parallel light rays emanate from the illuminator and remain parallel as they strike the surface of the object. In contrast, light from a standard backlight amplifies and interferes with each other, resulting in a diffuse reflection.
Read related post> What Is Telecentric Illumination?
How telecentric illumination realizes high contrast contours

Telecentric illuminators work by using high-quality optical glass lenses to keep the light rays of optical fiber or LED spotlights parallel. The divergent light emitted from the light source enters the glass assembly and becomes parallel and highly concentrated. Almost all the light that enters the telecentric illuminator (ignoring the back reflection and absorption of light by the various optical lenses) hits the object being detected.
In an original device, the diffuse reflection from a backlight causes blurred edges. When replaced with a telecentric illuminator, the edges become sharper, making it easier to determine whether or not they have passed the test. Additionally, while a standard backlight may render burrs on threaded surfaces almost invisible, a telecentric illuminator can easily detect and measure such imperfections. The images above illustrate the contrast between the telecentric illumination system and the standard backlight system. The greater the contrast, the higher the accuracy of the measurement.
Read related post> Auto Parts (Screw) Thread Detection
Advantages of telecentric illumination
There are some advantages of telecentric illumination:
- Unrivalled ability to detect minor defects
- Measurement accuracy and repeatability are higher than with standard backlighting
- It improves the light intensity of the parallel light, shortens the exposure time of the camera, and makes the system faster than the standard backlight
- It eliminates blurred edges and improves image contrast
- The distance between the object and the light source increases
Medical bottle cap inspection
To fully appreciate the significance of a telecentric system in machine vision, it is necessary to understand its principle and analyze how it is applied in real cases. The following solution shows how a telecentric system is used to efficiently inspect medical bottle caps.

Objects to be inspected:
medical bottle cap
Inspection requirements:
- Bottle caps with seams greater than 0.05mm are considered defective
- Large FOV of 100mm (diagonal)
- High precision, and low distortion
Solution:
- DTCM120-48-AL (DTCM series Bi-Telecentric Lenses)
- DTCL-48-1W-G (telecentric parallel backlight)
- 1/2.3″ camera
- DTCM48-cover glass


Inspection results:
- The resolution of the center and edge of the FOV is extremely high, and the distortion is extremely low;
- With parallel backlights, compared with traditional flat-panel backlights, the edges are sharper and the gray transition pixels are fewer. At the same time, the brightness of the centre and the periphery of the field of view remain uniform, which maximizes the high-resolution characteristics of the lens and greatly improves the accuracy of measurement;
- The effective aperture is F6.8, while the resolution is guaranteed, the depth of field also meets the project requirements.
Read related post> Pharmaceutical oral Liquid Bottle Inspection
Why do we choose the COOLENS®’ DTCM series Bi-Telecentric lenses in this solution?
There are different types of telecentric lenses, but for this application, a bi-telecentric lens would be a better choice. A bi-telecentric lens has both its entrance pupil and exit pupil at infinity. This means that it also eliminates perspective errors and magnification changes caused by variations in camera position or sensor size. Therefore, in this case, we chose COOLENS®’ DTCM series Bi-Telecentric Lenses, with a large FOV (26-300mm), suitable for sensors up to 67.6mm, 3.76μm cameras and telecentric illumination for high-resolution imaging. In addition, customizable aperture, various mount options, and more than 223 models are provided by VICO Imaging. So this is the best choice.
Conclusion
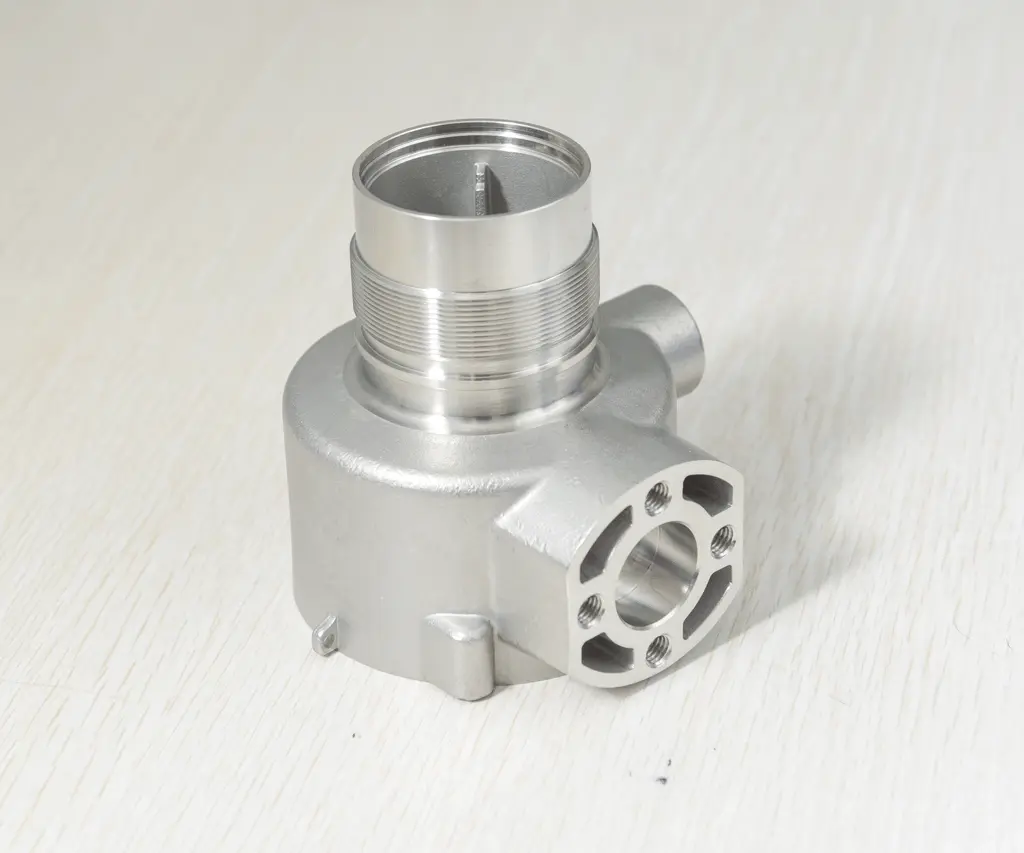
Telecentric lenses facilitate machine vision applications such as high-speed imaging, factory automation, display contours, defect and edge detection. As shown in the figures below, screws, valves, and bearings are common objects to be inspected in machine vision inspection scenarios.
Unlike standard backlights, telecentric lenses produce sharp contours that are particularly suitable for detecting edges and defects. This advantage is important for applications that require high-contrast, unblurred edge-free images and for high-speed automation applications.








