Recently, the use of Machine Vision technologies has rapidly increased in various applications. And its popularity has skyrocketed so much that it is found in almost every other industry.
The improvement of the camera, illuminations, and software components have also made it easier to capture clear images. Of course, these images are much better than those caught with lasers and other conventional methods.
As we know, high-quality optics can provide high-performance results. You must invest in high-quality telecentric lenses if you want precise magnification for a specific application.
So, what are telecentric lenses? How do these lenses work? How can you choose the right telecentric lenses for your upcoming work?
These questions have hindered a lot of people from using these lenses. But it will no longer be a major problem now.
This post will cover everything you should know about the telecentric lens and its usage. If you have little or no knowledge about telecentric lenses, take your time and read this article.
What Is Telecentric Lens?
Telecentric lenses are a special type of lens usually used to maximize imaging performance. They can also help to lower distortion and capture measurements accurately.
Let’s split the word telecentric for better understanding. The term ‘tele’ means distant or far. Likewise, the term ‘center’ refers to the pupil aperture in this context, i.e., the main center of an optical system.
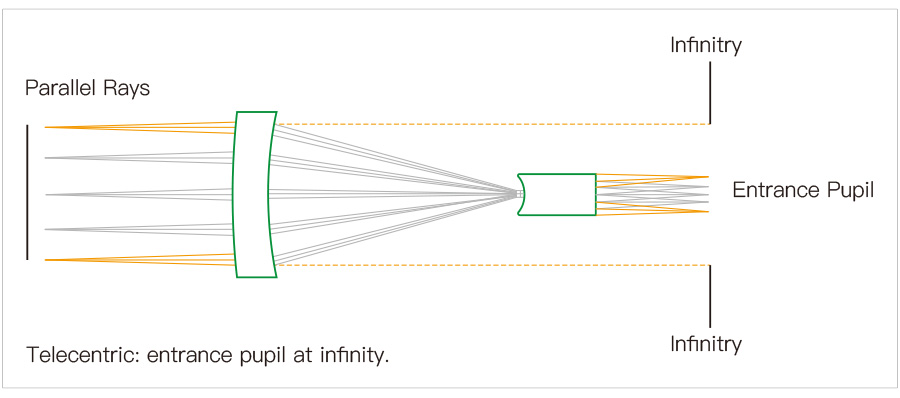
So in telecentric lenses, the stop aperture is precisely placed on the focal plane. As a result, the incoming rays focus on the entrance pupil. This entrance pupil appears as if it is virtually positioned at infinity.
These lenses are often used for long-distance cameras to capture clear images. Besides, telecentric lenses can provide a sharper field view of an image.
Before we proceed further, you must understand the basic theory behind image capturing. And also how the telecentric lens captures magnificent shots.
As the name suggests, the rays of the telecentric lens travel through the middle of the parallel aperture. It can settle either at the back or in front of the vision system. Then, the settled ray in the lens goes into tiny imagery particles.
Thus, telecentric lenses are ideal for various machine vision applications where the distance between the target and the camera is quite long.
Telecentric lenses are also suitable for applications that require precise measurements or accurate alignment.
These lenses have a unique optical design that keeps the size of the object image constant. It does this regardless of the distance between the lens and the object.
So this makes them particularly useful in metrology, quality control, and inspection. Besides, many companies use them for machine vision applications that need precise measurements of an object’s size or position.
Additionally, telecentric lenses have low distortion. It makes them ideal in applications where accurate alignment is essential. For instance, you will find them in robotics, 3D scanning, and other automated systems. These lenses are also used in the field of microscopy.
What Are the Characteristics of Telecentric Lenses?
Ordinary non-telecentric lenses may not be suitable for machine vision applications. That’s because they cannot perform repeatable, highly-accurate measurements quickly.
Instead, telecentric lenses achieve the highest possible accuracy. Let’s discuss the exceptional characteristics of telecentric lenses.
1. Constant Magnification
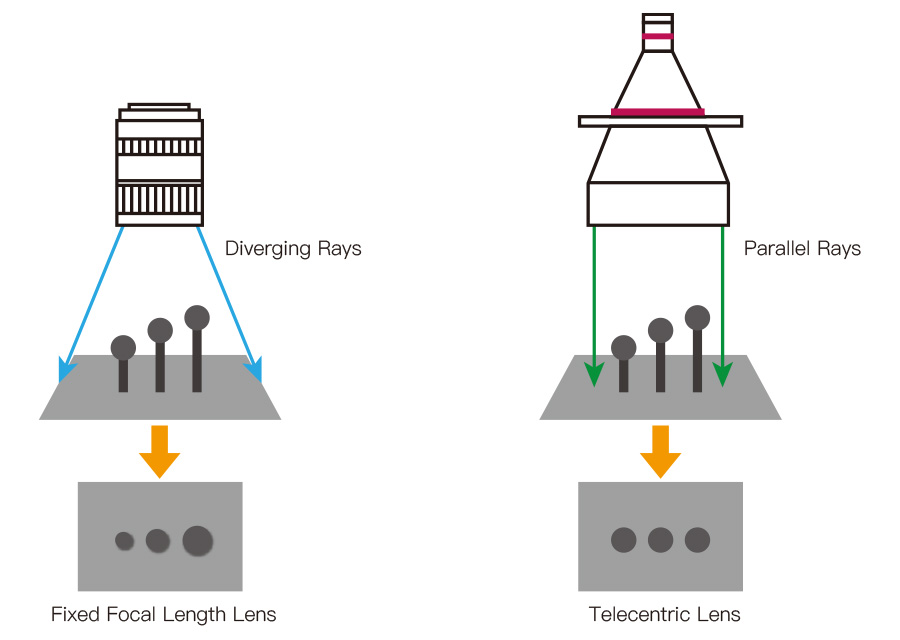
Ordinary lenses provide varying magnifications at various conjugates. So, the object’s image size changes almost proportionally when you displace the object.
With telecentric lenses, an object’s image size will remain the same regardless of the object’s distance from the lens.
It is useful in measurement applications, as the image size will not change. That’s because this feature makes it easier to take accurate measurements.
2. High Depth of Field
Because the entrance pupil is far away, the depth of field is much greater than a standard lens. It is helpful in applications that need a considerable field depth, such as machine vision systems.
3. Reduced Perspective Distortion
Distortion is a common issue that can limit measurement accuracy. Remember, it can impact even the best-performing optics.
Ordinary optics have different distortion values, making it challenging to get precise measurements. Moreover, things can get even more destructive with non-telecentric lenses.
Since the entrance pupil is far away, perspective distortion reduces in telecentric lenses. It is helpful in applications where perspective distortion needs to be reduced, such as architectural photography.
4. High Resolution
Telecentric lenses have high resolution across the entire field of view. It makes them useful in applications that require high resolution, for example, microscopy, metrology, and machine vision.
5 No Uncertainty
It is challenging to determine the actual position of the object’s edges, especially when there is backlighting. It happens because the object’s dark pixels overlap with the illuminated pixels in the background. Telecentric lenses can overcome this effect and offer a clearer image.
In short, telecentric lenses have many unique characteristics that make them ideal in different applications.
What Are the Different Types of Telecentric Lenses?
Telecentric lenses aren’t limited to one type. It comes in three broad types: object-space telecentric lens, image-space telecentric lens, and Bi-telecentric lens.
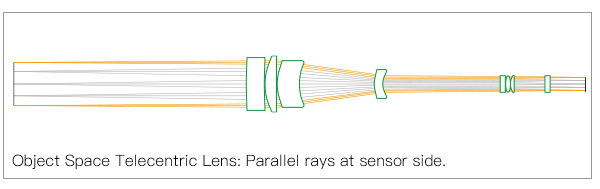
1) Object Space Telecentric Lens
This telecentric lens mounts the aperture diaphragm on the space focal plane of the image.
When the lens’s aperture diaphragm is on the camera, the distance of the edge of the image will change. However, that doesn’t mean that the height of the image will change.
In short, this type of lens can capture the image while keeping the measured object size intact. Thus, the object space telecentric lens is suitable for industrial applications requiring low distortion.
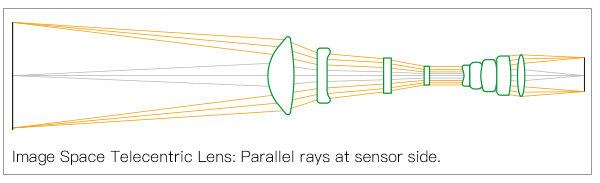
2) Image Space Telecentric Lens
The distance between the image sensor or film and the lens doesn’t matter in image-space telecentric lenses. These lenses can still create images of the same size.
The exit pupil is at infinity in image-space telecentric lenses. As a result, the lens can focus on different distances and create an image without affecting the size.
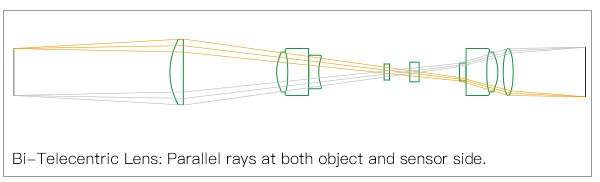
3) Bi-Telecentric Lens
The bi-telecentric lens is a unique type that merges the features of both the object space and image-space telecentric lenses.
These lenses are consistent and precise. Moreover, they have low distortion, a large depth of field, and high magnification. Bi-telecentric lenses are used for both industrial and machine vision image processing.
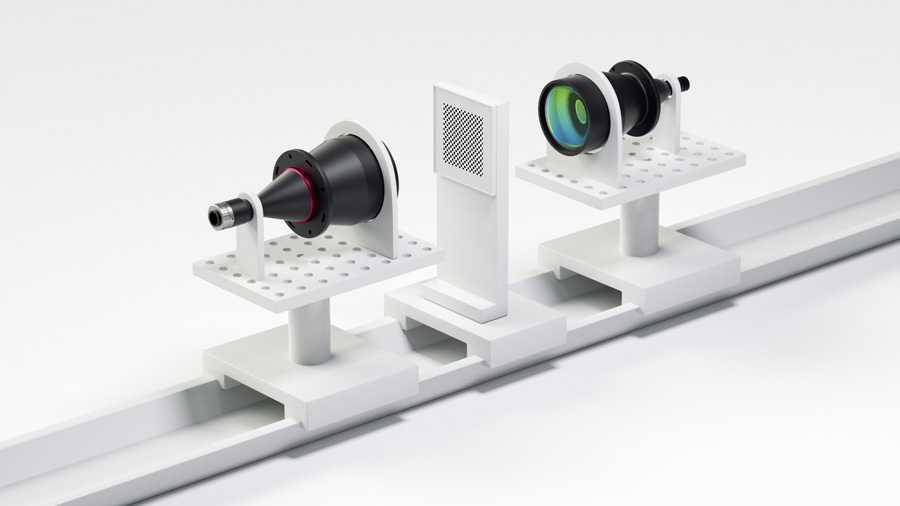
How Do Telecentric Lenses Work?

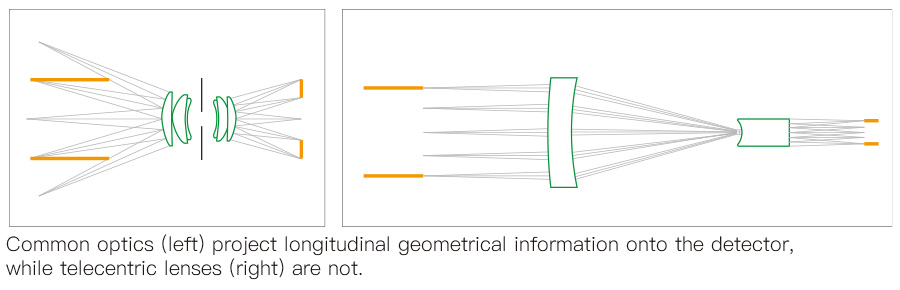
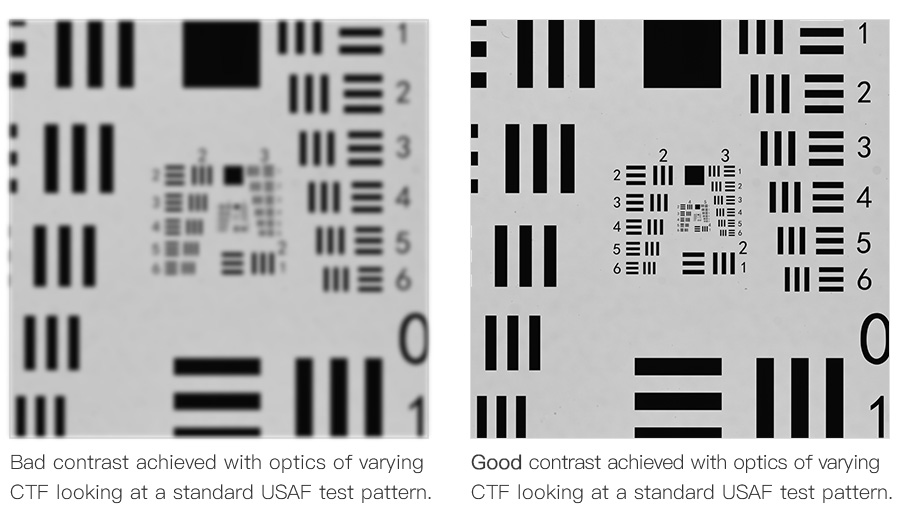
Telecentric lenses reduce the edge angle of the image sensor and light rays. With this, it produces little to no distortion and improves the quality of the image that is being captured.
In ordinary optics, the light rays usually bend at different angles when they exit the lens. However, a telecentric lens works differently. It keeps all light rays parallel after leaving the lens.
You can quickly see the difference by comparing the images captured by ordinary and telecentric lenses. You will notice that images captured by telecentric lenses have greater precision and detail.
Moreover, the unique parallel position of light rays allows telecentric lenses to focus on distant objects.
Now, you might wonder how telecentric lenses work and capture precise images. Well, the secret lies in the making of telecentric lenses.
In telecentric lenses, two lenses are placed together with different focal lengths. The first lens takes the light from the object being captured. After that, it focuses the light on the second lens.
Lastly, the second lens projects the light to the back end of the device, i.e., the diaphragm. This device controls the amount of light entering the sensor. It ensures only light rays parallel to its surface can pass.
As a result, you get precise images since all aberrations driven by off-axis rays get eliminated. It is something not achievable with ordinary lenses.
How Are Telecentric Lenses Different from Conventional Lenses?
You should know how telecentric lenses differ from conventional/traditional lenses.
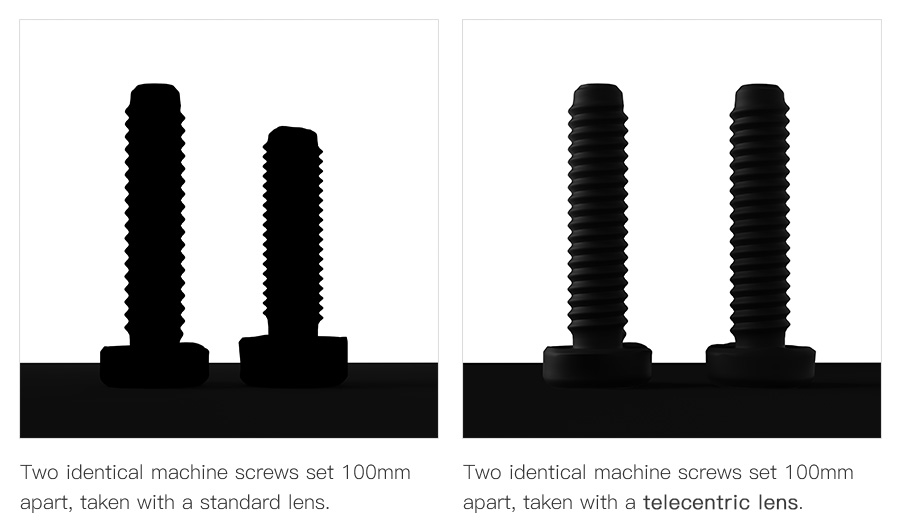
Magnification is the main point of comparison here. As you know, magnification depends on the distance between the lens and the object.
Conventional lenses have an angular field view of images when they are captured. Thus, the farther the distance between the camera and the object, the smaller it becomes in size.
So, if you want your object magnified with a conventional lens, you must get closer to the object. Unfortunately, this angular field view increases the chances of an image parallax, also known as perspective error.
However, the telecentric lens is the total opposite of the conventional lens. The angle of the field view is not a determinant of the distance, height, or size.
Moreover, the distortion values in telecentric lenses are low compared to ordinary lenses.
When Should Telecentric Lenses be Used?
The usage of Telecentric lenses is not just limited to just one or two needs.
There are different times when telecentric lenses can give you better results than ordinary lenses. Below are some scenarios when you can employ telecentric lenses.
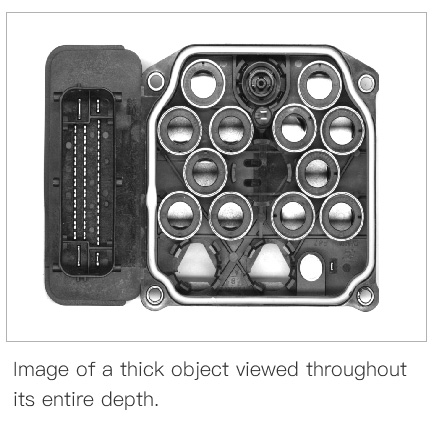
- Use telecentric lenses when you need to measure a thick or heavy object. Telecentric lenses can perform better if the object’s thickness is greater than 1/10 FOV diagonal.
- You can use telecentric lenses when there is a need to capture different edges and sizes of an object.
- Telecentric lenses are the best choice when you are unsure of the distance between the camera/telecentric lens and the object you want to capture.
- These lenses are suitable when there is a need to measure or inspect the size of a hole.
- Telecentric lenses are preferred when you want to extract or condense the profile of the object you want to capture.
- Use telecentric lenses when you want an even tone of the brightness of the object that you want to capture.
- Telecentric lenses can perform better when the image requires a directional field view.
All these and more are some of the cases when you should use your telecentric lenses.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Telecentric Lenses?
So far, you have seen many advantages of telecentric lenses. While talking about the high side of Telecentric Lenses, we should not also forget that there are downsides to it.
Of course, these downsides are negligible. But it doesn’t mean we should refrain from mentioning them.
So, this section will include the telecentric lens’s advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
1) Ultra-wide Depth of Field
The first advantage is their depth of field, which is ultra-wide. It means you can focus on the object you want to capture from various angles. Moreover, it helps in situations where the image is captured from three dimensions.
2) Low Distortion
Another advantage of telecentric lenses is low distortion. It means that the output image is a close replica of the object with minimal distortion or blurring.
In general, low distortion indicates a high signal integrity and accuracy level.
As discussed above, distortion is a common issue in lenses. It affects measurement accuracy. Also, even top-level optics are impacted by some degree of distortion.
High-quality telecentric lenses offer a shallow distortion degree. So, if high-level image quality is what you desire, telecentric lenses are your best bait.
3) Unique Parallel Line Design
Not everyone cares about the parallel line design of their images. But, to those that do, it is a big deal.
Unlike conventional lenses, telecentric lenses have fantastic, unique parallel line designs that make the image look better.
It is one of the features that draw a lot of lens enthusiasts to telecentric lenses.
4) Resistant to Aberrations
Telecentric lenses also have aberration resistance. In short, these lenses can produce more precise and sharper images with zero distortion.
Disadvantages
1) High Cost
The telecentric lenses are the improved version of ordinary lenses. These lenses use advanced technology. Besides, the lenses are made of expensive materials.
Thus, telecentric lenses are expensive. As a result, not a lot of people can afford telecentric lenses.
2) Large Size
Telecentric lenses are large and not so portable. You might not be able to carry your telecentric lens if you do not have plans to bring a big bag pack.
3) Weight
Another disadvantage of telecentric lenses is that they are heavy. And, most times need extra power and strength to carry them around.
As you can see, the advantages of telecentric lenses beat the disadvantages. So, we recommend you focus on the positive aspects of telecentric lenses before buying them.
What Are the Applications of Telecentric Lenses in the Machine Vision Industry?
Quality control and inspection are two major processes followed in manufacturing. Nowadays, many industries are relying on advanced technologies to perform these operations. And machine vision industry is not an exception to it.
Some of the applications of telecentric lenses in the machine vision industry are as follows:
- Production of medical devices and materials.
- The manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries.
- Textile industry
- Production of automotive parts.
- Manufacture of semiconductors.
- Printing and solar power industries
- Production of mobile components.
- Manufacturing of 3C electronics.
The machine vision industry also packages, tracks, and performs maintenance robotically.
 |
 |
 |
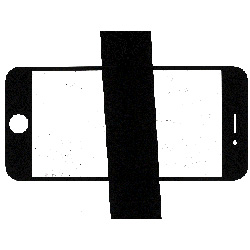 |
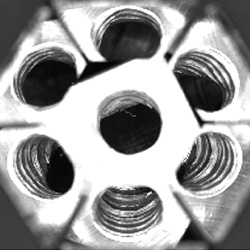
| Bottle mouth and bottle size detection. | QR code and number detection on the front of mobile phone battery. | Inspect the presence of internal screw thread. | Smart phone glass screen size measurement. |
 |
 |
 |
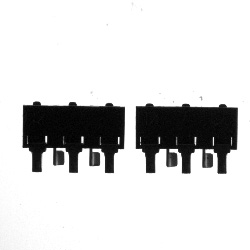 |
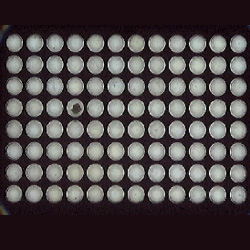
| Check if the pins are missing and crooked. | Recorded movement trajectory. | Measure the number of biological reagents. | Detects whether the pins are bent, or missing.Detects pin alignment. |
Telecentric lens is a vital element of the machine vision industry. It provides the machine with a ‘vision’ as clear and sharp as you can imagine.
Furthermore, there are other ways that telecentric lenses can be used. They can be utilized for cameras, as well as microscopes.
For instance, when you want to achieve accuracy, ensure you capture the object’s tiniest details. It is only possible when you use telecentric lenses.
Also, these lenses can be used to inspect objects and other materials. It is done through the magnification features of the telecentric lens.
Even in medical fields, organs and body tissues are viewed and captured with telecentric lenses. As you can see, the applications of telecentric lenses are vast.
How to Choose the Right Telecentric Lenses?
People often ask what to look for when choosing the right telecentric lens. They particularly emphasize the ‘type’ of the lens.
Choosing the right telecentric lens can be tricky. Of course, you don’t want to make mistakes or waste money on a lens that won’t serve you.
So, to avoid choosing the wrong lens, look for the following components and features.
1) CCD target surface size
Don’t worry; we’ll explain this term better. While selecting your telecentric lens, the CCD target surface should either be bigger or equal in size to the surface target of the camera.
Otherwise, the resolution won’t be compatible and will go to waste.
2)The type of interface
If you give an up-close look, you’ll realize that the telecentric lens’s interface is almost identical to that of the regular lenses. Hence, you must consider the interface type before purchasing.
3) Magnification
The range of imaging is determined according to the CCD target surface. For better magnification, the object should remain within a specific range, i.e., the telecentric range.
4) Depth of field’s range
It has to do with the optical characteristics of the field and the size of the field. It is determined by the wavelength and F number of the lens. Telecentric lenses often have a large and more adjustable depth of field than ordinary lenses.
5) Focal Length
The focal length of a telecentric lens matters a lot. Make sure you calculate the focal length. Your calculation would depend on your capturing distance from the object.
The fixed focal length lenses often have an angular field of view. It results in objects being imaged smaller. You can check our collection of fixed focal length lenses.
That’s why you need telecentric lenses for long-distance applications.
6) Sensor Type
When looking for the sensor type, you should choose between CCD and CMOS. Although in recent times, the differences between them have literally gone extinct.
However, in terms of high-quality imaging and sensitivity, it’d be ideal to go for the Charge-Coupled Device (CCD).
Also, for speed and better integration, Complimentary-Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) will be your best choice.
7) Frame Rate
The achievable frame rate is often affected by the camera output. Thus, you must be sure of the lens and camera compatibility before you go for it.
8) Color or Monochrome Camera
Vision systems often make use of color cameras. Yet, there are others that utilize monochrome. They use monochrome because they are way cheaper than color cameras.
But, if you want to detect abnormalities and defects during the quality inspection, you must prefer color cameras. The telecentric lenses can offer precise color representation for a long-distance object.
9) Price
Last but not least, you should also consider the price of the telecentric lens.
The lens might fulfill the above points, but the cost alone can become your primary concern. Before setting out, we recommend you do a market survey about the prices of the telecentric lenses.
Where Can You Buy High-Quality Telecentric Lenses?
Many people ask about where they can purchase high-quality telecentric lenses. If you are unsure, this section will give you the correct answer.
At VicoImaging, we provide you with the best, most effective, and budget-friendly telecentric lenses. We have tons of testimonies from customers who have a lot of amazing things to say about our high-resolution telecentric lenses.
We can offer you the best lenses at a very affordable price.
What more?
The best part is that our telecentric lenses are not imported. Instead, they are manufactured in-house with a guarantee and warranty.
Our lens collection allows you to choose from various tested designs based on what fits your application best.
Feel free to inform us about your application needs. Be it field of view, wavelength, or improved imaging! We can optimize our existing designs to meet your specific requirements.
With this, you can dodge the hassle of designing a new telecentric lens fully from scratch. Moreover, you can also reduce or remove design fees.
So, go ahead and browse our collection of telecentric lenses. You can also talk to VicoImaging support team for custom orders.
FAQs:
1) Can We Improve the Dof of a Telecentric Lens?
Of course, yes! It is possible to improve the DoF of a telecentric lens. You can change the DOF of a telecentric lens by changing its aperture.
Remember, the DoF and aperture are inversely proportional. It means when the aperture gets larger, the DoF will become smaller.
2) Why Are Telecentric Lenses Used in Machine Vision Applications?
Telecentric lenses are commonly used in machine vision systems in various ways. Some machine vision applications have unique needs.
So, telecentric lenses can help measure objects in three dimensions. Moreover, these lenses are helpful in tasks like inspecting big objects and checking the fine details of tiny objects.
Since telecentric lenses have a vast field of view, they can view the whole object in one image. As a result, identifying defects becomes easier.
Likewise, telecentric lenses also have a large magnification. It helps assess fine details on tiny objects, like dents or scratches.
3) What Is Telecentric Illuminator?
Telecentricity is a common term used in imaging optics. It refers to a unique lens design with parallel chief rays across the field of view.
To achieve this, the aperture stop is placed in the lens assembly to obstruct all off-axis light. Thus, it can only emit light that is parallel to the imaging axis.
When we apply this principle to illumination, it results in a collimated light beam with lower divergence and excellent uniformity. The device that helps achieve this is called a telecentric illuminator.
Final Thoughts!
Telecentric lenses have become an integral part of machine vision systems. That’s because they have a long working distance and large magnification.
Ordinary lenses often exhibit common issues, affecting the image processing experience. It includes poor image resolution, positional uncertainty of an object edge, perspective errors, and image distortion. Even more, ordinary lenses cannot stand for proper magnification when an object is displaced.
Telecentric lenses can reduce or even eliminate all such issues. They can achieve a high grade of accuracy and precision in imaging systems.
VicoImaging manufactures a broad range of telecentric lenses in different parameters. You can use our proficient telecentric lens customization service if you have unique needs.








4 thoughts on “A Beginner’s Guide to Telecentric Lenses and Their Applications!”
If the object were in infinity,can we use Image Space Telecentric Lens that have several degrees of FOV?
Yes, you can, An ideal convex lens with an infinite focal length can meet this requirement. In reality, you need to find an image space telecentric lens with an infinity focal length.
Hi David, the part of your reply after the “yes, you can” is wrong : a lens with an infinite focal length would have no curvature, it would be a window.
Windows however do not map objects to images, which is the _definiting property_ of a lens. Therefore lenses with infinite focal length do not exist. What you mean is a designed focus _distance_ of infinity.
_All_ image generating lenses are equivalent to a thick, convex lens. So the word “convex” can be skipped here.
Best regards
Micha
Michael thank you for pointing out the error in our previous description. In optics, convex lenses indeed represent a positive focal length, and only lenses with a positive focal length can image objects at infinity onto the image plane, hence the term “convexity” cannot be omitted. However, the statement regarding using a lens with an infinite focal length to image an object at infinity is incorrect. The accurate statement is that an infinite object distance, finite focal length, and image-side telecentric lens can be utilized, and a lens with a finite focal length on the image-side telecentric lens has a certain field of view angle (our DTCM’s field of view angle is 12 degrees).
We sincerely apologize for the inaccuracies in our previous description and appreciate your correction. We are committed to continually improving our content to ensure accuracy and clarity. If you have any further questions or require additional clarification, please feel free to reach out to us. Thank you once again for your valuable feedback.